Accelerating the transition and commercialization of energy technologies in every sector – renewables, efficiency, fossil, nuclear and crosscutting – is important not only in meeting state and national energy and environmental goals, but also in creating new economic opportunities. For this reason, nearly one in four State Energy Offices across the country is involved in energy technology transition activities, ranging from early-stage research to commercialization and deployment. State Energy Offices are pioneering innovation-driven state policies and programs by leveraging their networks, policy expertise, resources, and clout to help inventors, entrepreneurs, and start-up businesses deliver energy technologies to the marketplace.
A state’s “Energy Innovation Ecosystem” is often a vast network encompassing entrepreneurs, start-up businesses, incubators, academia, public and private investors, and deployment partners supporting the development and expansion of advanced energy markets. This ecosystem also captures a wide array of activities, including early-stage research, technology development and demonstration, commercialization, and mainstream market deployment.
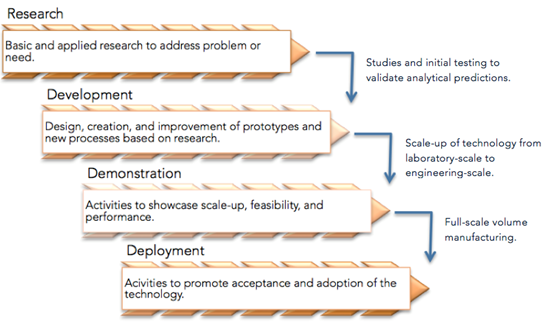
State Energy Offices and other policy makers can play a crucial role in ensuring that their state has a competitive and transparent environment for energy innovation and technology advancement to thrive. Some of the major policy, program, and funding mechanisms that states have used to
Here’s how some NASEO members are helping to grow the Energy Innovation Ecosystem:
 Virginia: Commonwealth Energy Fund
Virginia: Commonwealth Energy Fund
Virginia’s Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy (DMME) and the Center for Innovative Technology (CIT) launched the Commonwealth Energy Fund (CEF) in 2011 to make loans to high-growth-potential early-stage Virginia energy companies. A debt-to-equity investment program, CEF initiatives as debt and, at CIT’s option, can convert downstream to equity. CIT and DMME use the expertise and guidance of the CEF Investment Advisory Board to advise and support their client companies, which advance technologies that are strategic to Virginia’s energy goals.  California: Electric Program Investment Charge
California: Electric Program Investment Charge
The Electric Program Investment Charge (EPIC) is designed to assist the development of non-commercialized new and emerging clean energy technologies in California through applied research and development ($55 million/year); technology demonstration and deployment ($75 million/year), and market facilitation and workforce development ($15 million/year). The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) oversees EPIC’s implementation, 80% of which is administered by the California Energy Commission (the State Energy Office) and the remaining 20% by three electric investor-owned utilities. Texas: Emerging Clean Energy Incubator Emerging Technology Program
Texas: Emerging Clean Energy Incubator Emerging Technology Program
Through the Clean Energy Incubator Emerging Technology Program, the Texas State Energy Conservation Office (SECO) supports the development and sustainability of clean energy incubators located at higher education campuses.
Share your state’s innovation success stories by contacting Sandy Fazeli (sfazeli@naseo.org)!
Additional Information and Resources
To learn more: Contact Sandy Fazeli, Managing Director, Policy, or Sam Cramer, Senior Program Manager.